"LAMP" stands for Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification. This technology was developed by Notomi et al. It is a very sensitive, easy and time efficient method. The LAMP reaction proceeds at a constant temperature using a strand displacement reaction.
Types of Primers used in LAMP
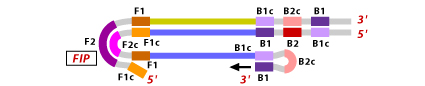
LAMP is characterized by the use of 4 different primers specifically designed to recognize 6 distinct regions of the target gene. The four primers used are as follows:1. Forward Inner Primer (FIP): The FIP consists of a F2 region at the 3'end and a F1c region at the 5'end. The F2 region is complementary to the F2c region of the template sequence. The F1c region is identical to the F1c region of the template sequence.
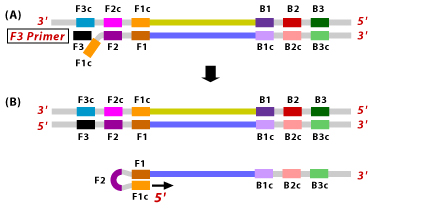
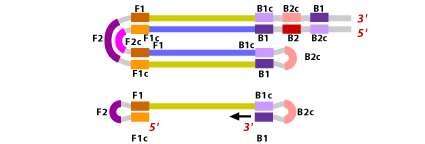
2. Forward Outer Primer (FOP): The FOP (also called F3 Primer) consists of a F3 region which is complementary to the F3c region of the template sequence. This primer is shorter in length and lower in concentration than FIP.
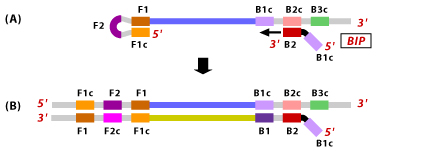
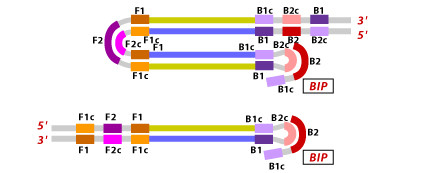
3. Backward Inner Primer (BIP): The BIP consists of a B2 region at the 3'end and a B1c region at the 5'end. The B2 region is complementary to the B2c region of the template sequence. The B1c region is identical to the B1c region of the template sequence.
4. Backward Outer Primer (BOP): The BOP (also called B3 Primer) consists of a B3 region which is complementary to the B3c region of the template sequence.
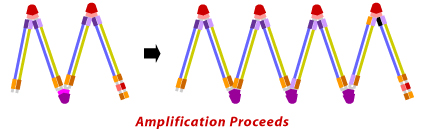
Stages in Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification
1. F2 region of FIP hybridizes to F2c region of the target DNA and initiates complementary strand synthesis.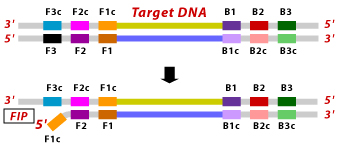
3. This single stranded DNA with
a loop at the 5' end serves as a template for BIP. B2 hybridizes to B2c
region of the template DNA. DNA synthesis is now initiated leading to
the formation of a complementary strand and opening of the 5' end loop.
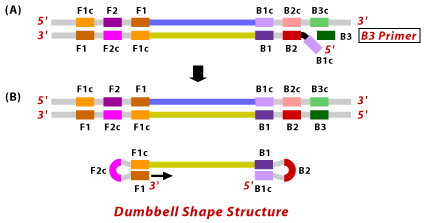

Lamp Detection
In a LAMP assay, the reaction takes place in a single tube containing buffer, target DNA, DNA polymerase and primers. The tube is incubated at 64°C in a regular laboratory water bath or heat block that helps in maintaining a constant temperature. The amplified product can be detected by naked eye as a white precipitate or a yellow-green color solution after addition of SYBR green to the reaction tube.Advantages
1. Amplification of DNA takes place at an isothermal condition (63 to 65°C) with greater efficiency.2. Thermal denaturation of double stranded DNA is not required.
3. LAMP helps in specific amplification as it designs 4 primers to recognize 6 distinct regions on the target gene.
4. LAMP is cost effective as it does not require special reagents or sophisticated equipment.
5. This technology can be used for the amplification of RNA templates in presence of reverse transcriptase.
6. LAMP assay takes less time for amplification and detection.
Applications
1. LAMP is used in rapid diagnosis of viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases.2. It helps in the identification of genus and species-specific parasites.